在 ETL 过程中,我们时常需要知道这些数据是从哪些表的哪个字段来的。我们可以写一个文档,但文档需要时刻维护。如果是用一些 ETL 工具,可是直接画出这些关系,即数据血缘。在我的项目中,由于是自己造轮子,所以需要自己画数据血缘,如下图所示。
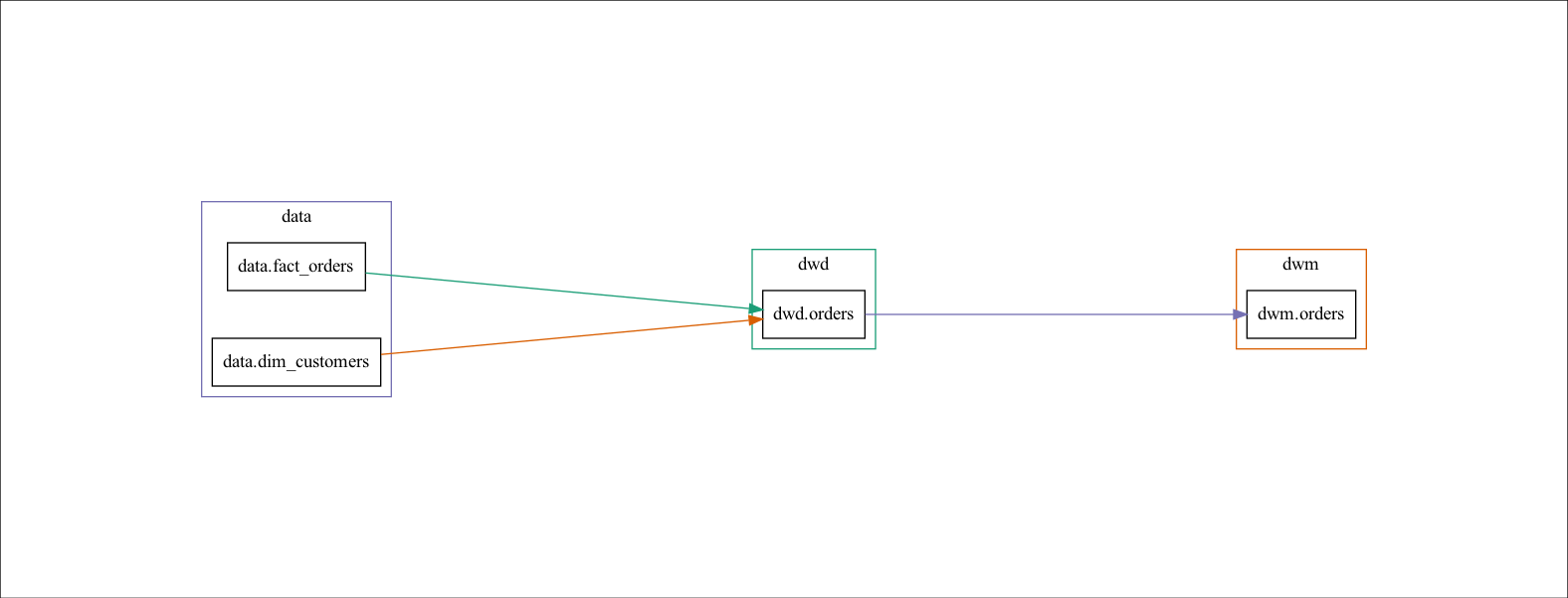
自己写了一段代码,主要是通过解析 sql 语句,然后在用 Python 的 DOT language 来实现的。
实现代码
import re
import os
from collections import defaultdict
import json
import pydot
def parse_relationships_from_sql_files(sql_folder_path):
full_relationships = []
for root, _, files in os.walk(sql_folder_path):
print(files)
for file_name in files:
if file_name.endswith('.sql'):
print(file_name)
full_relationships += parse_relationships_from_sql_file(sql_file_path=f"{root}/{file_name}")
return full_relationships
def parse_relationships_from_sql_file(sql_file_path):
"""
return:
[
{'staging': {'dim_customers': [('app', 'account')]}},
{'data': {'dim_customers': [('staging', 'dim_customers'),
('data', 'dim_customers')]}},
{'data': {'dim_customers': [('staging', 'dim_customers')]}}
]
"""
sql = ''
sql_raw_relationships = []
with open(sql_file_path) as file:
sql = file.read()
sql_statements = parse_sql_statements(sql)
for statement in sql_statements:
relationship = parse_insert_statement(statement)
sql_raw_relationships.append(relationship) if relationship is not None else None
relationship = parse_update_statement(statement)
sql_raw_relationships.append(relationship) if relationship is not None else None
return sql_raw_relationships
def parse_sql_statements(sql):
sql_match = re.search(r"CREATE.+FUNCTION[\s\S]*(?<=BEGIN)([\s\S]*)(?=END)", sql)
sql_statements = [x.strip() for x in sql_match.group(1).split(';')] if sql_match else []
return sql_statements
def parse_insert_statement(sql):
"""
return:
{'data': {'dim_customers': [('staging', 'dim_customers')]}}
"""
# Extract target table and columns
target_table_match = re.search(r"INSERT INTO\s*(\w+\.\w+)\s*\(([^)]*)\)", sql, re.IGNORECASE)
target_table = None
target_columns = None
if target_table_match:
target_table = target_table_match.group(1)
target_columns = [col.strip() for col in target_table_match.group(2).split(',')]
else:
return None
# Extract source table and columns
source_tables = list()
source_table_match = re.findall(r"FROM\s+(\w+\.\w+)\s(\w+)", sql, re.IGNORECASE)
if source_table_match:
source_tables += source_table_match
join_tables = re.findall(r"JOIN\s+(\w+\.\w+)\s(\w+)", sql)
if join_tables:
source_tables += join_tables
source_columns_match = re.search(r"SELECT\s+(.+)\s+FROM", sql, flags=re.DOTALL | re.IGNORECASE)
source_columns_str = source_columns_match.group(1).strip() if source_columns_match else ""
source_columns = [col.strip() for col in source_columns_str.split(',')]
if target_columns and source_columns:
pass
schema, table = target_table.split('.')
relationship = {
schema: {
table: [tuple(tbl.split('.')) for tbl, _ in source_tables]
}
}
return relationship
def parse_update_statement(sql):
"""
return:
{'data': {'dim_customers': [('staging', 'dim_customers')]}}
"""
# Extract target table and columns
target_table_match = re.search(r"UPDATE\s+(\w+\.\w+)", sql, re.IGNORECASE)
target_table = None
if target_table_match:
target_table = target_table_match.group(1)
else:
return None
# Extract source table and columns
source_tables = list()
source_table_match = re.findall(r"FROM\s+(\w+\.\w+)\s(\w+)", sql, re.IGNORECASE)
if source_table_match:
source_tables += source_table_match
join_tables = re.findall(r"JOIN\s+(\w+\.\w+)\s(\w+)", sql)
if join_tables:
source_tables += join_tables
schema, table = target_table.split('.')
relationship = {
schema: {
table: [tuple(tbl.split('.')) for tbl, _ in source_tables]
}
}
return relationship
def merge_relationships(relationships):
"""
return:
{
'app': {'account': []},
'staging': {'dim_customers': [('app', 'account')]},
'data': {'dim_customers': [('staging', 'dim_customers')]}
}
"""
merged_relationships = defaultdict(lambda: defaultdict(list))
for relationship in relationships:
for schema, tables in relationship.items():
for table, sources in tables.items():
for source in sources:
src_schema, src_table = source
# skip self table to self table scenario
if (src_schema == schema) and (src_table == table):
continue
# just initialize this node
if merged_relationships[src_schema][src_table]:
pass
if source not in merged_relationships[schema][table]:
merged_relationships[schema][table].append(source)
return merged_relationships
def generate_dot_for_relationships(relationships):
dot_content = "digraph dw { rankdir=LR;\n graph [pad=2.0, nodesep=0.5, ranksep=4];\n splines=true;\n colorscheme=dark28;\n "
relationship_dot = []
# draw the nodes for each schema as subgraph
for index, (schema, tables) in enumerate(relationships.items()):
schema_dot = f"subgraph cluster_{schema} " + '{' + "label=\"{schema}\"; shape=box; color={index+1}; "
for table, sources in tables.items():
schema_dot += f" {schema}_{table}[shape=box,label=\"{schema}.{table}\"]; "
for src_schema, src_table in sources:
relationship_dot.append((src_schema, src_table, schema, table))
schema_dot += "}\n"
dot_content += schema_dot
# draw the arrow between nodes
for idx, r_dot in enumerate(relationship_dot):
src_schema, src_table, schema, table = r_dot
# idx = list(relationships.keys()).index(src_schema)
dot_content += f"\n{src_schema}_{src_table} -> {schema}_{table}[color=\"/dark28/{(idx % 8)+1}\"];"
dot_content += "}"
return dot_content
def export_dot(dot_content, output_file):
graphs = pydot.graph_from_dot_data(dot_content)
graph = graphs[0]
graph.write_png(output_file)
folder_path = 'sqls/'
relationships = merge_relationships(parse_relationships_from_sql_files(folder_path))
print(json.dumps(relationships, indent=4))
dot_content = generate_dot_for_relationships(relationships)
export_dot(dot_content, 'assets/images/dw_data_flow.png')