对于Q&A类的问题,Bert显得就像一个差等生,几乎不知道我问的是什么。那如何解析问答对里面的答案呢?
Roberta
在Hugging Face的QA任务里面,排名第一的模型是一个基于Bert的模型RoBERTa。它可以做到简单的Q&A。
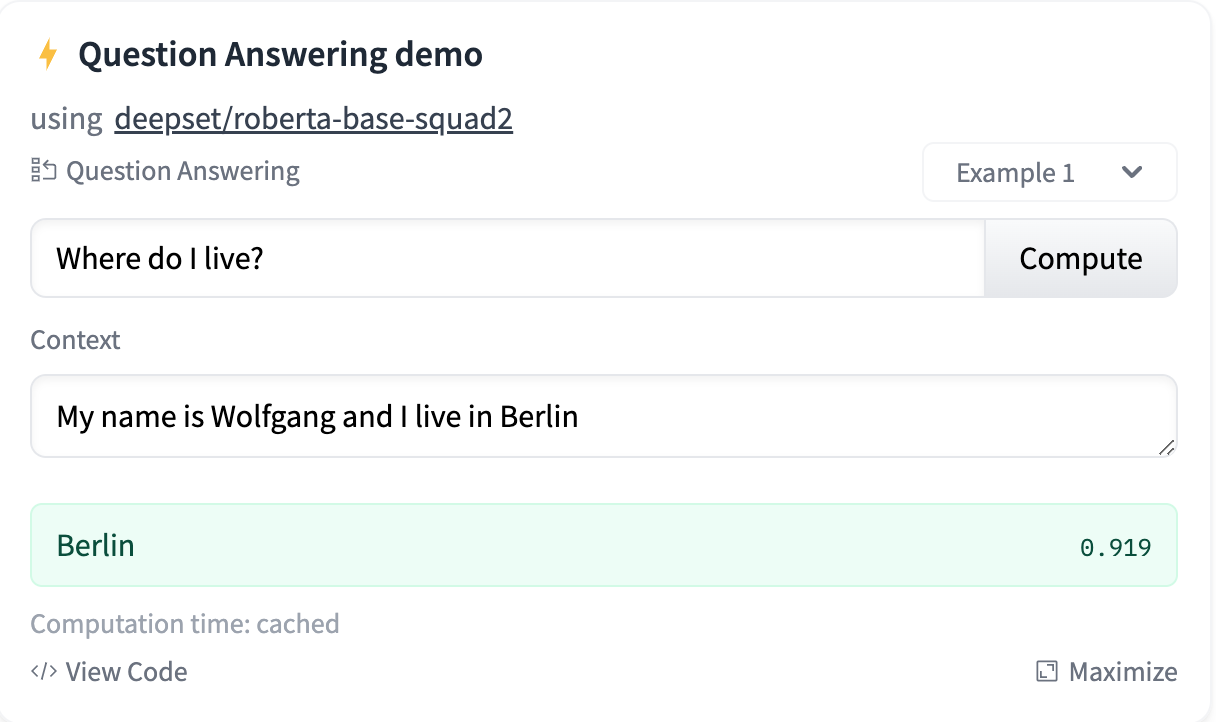
RoBERTa是源自RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach,基于之前我们用的BERT模型。而完成问答任务的模型deepset/roberta-base-squad2,则是RoBERTa基于SQuAD2.0进行预训练的模型。所以对于问答任务,它能够更好的理解问题。
解析问答对里面的答案
在打造个人助理里面,有很多问题需要解决,其中一个问题是对缺失信息的补充。机器人会针对缺失的信息进行提问,但我们没法保证收到的回复都是符合要求的,甚至可能是答非所问的。
比如下面的问答对,我希望能够识别到第二个医生Dr Aftab Moosa。
Q: Who do you wish to schedule the meeting, Dr Catherine Yang, Dr Aftab Moosa or Dr Bharat Agrawal?
A: the second one
如何Fine tuning
针对上面的任务,我们可以把问题转换为
question: what's the answer?
context: Q: Who do you wish to schedule the meeting, Dr Catherine Yang, Dr Aftab Moosa or Dr Bharat Agrawal? A: the second one
当然原来的SQuAD2.0没有这样的数据,模型肯定回答不满意。
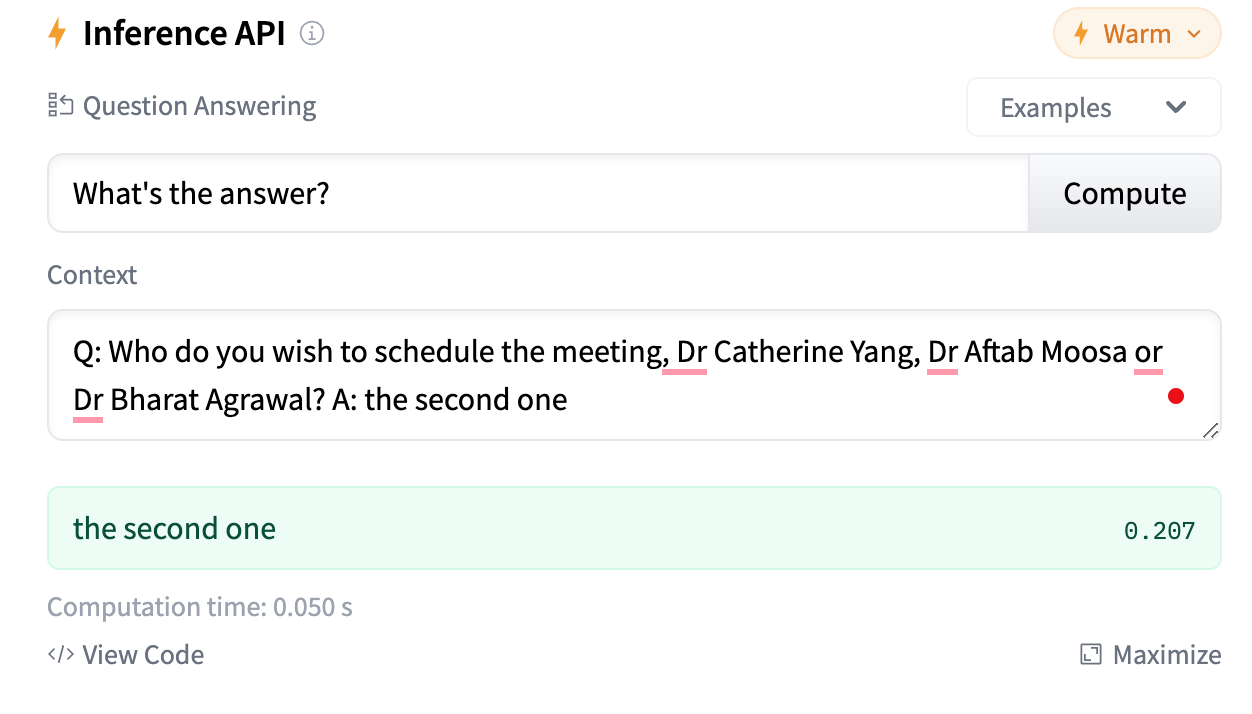
所以我们提前准备一些类似的数据,再进行微调,就可以完成上面的任务。
首先,引入deepset/roberta-base-squad2模型和tokenizer。
import torch
import os
import logging
import numpy as np
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoTokenizer, AdamW
from transformers.models.roberta import RobertaPreTrainedModel, RobertaModel
import torch.nn as nn
model_name = 'deepset/roberta-base-squad2'
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_name)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
roberta = RobertaModel(config=config)
并且引入qa_outputs层,用来微调模型。这里的config.num_labels为2,因为该任务将判断答案的开始位置和结束位置。
这里需要特别注意一下,虽然引入了num_labels=2的层,但不是对每个token进行二分类,而是为了判断答案的开始位置和结束位置。
qa_outputs = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_labels)
tokenize一下问题和上下文,可以拿到input_ids, token_type_ids和attention_mask。
question = "What is the answer?"
text = "Q: Who do you wish to schedule the meeting, Dr Catherine Yang, Dr Aftab Moosa or Dr Bharat Agrawal? A: the second one"
inputs = tokenizer(question, text, max_length=128, return_tensors="pt", padding="max_length",
truncation=True, return_offsets_mapping=True, return_token_type_ids=True)
inputs
这里多了一些额外的参数。max_length是最长为128个token,即输入的问题和上下文在embedding之后的大小。return_offsets_mapping还返回了input_ids里面每个token对应原始输入的偏移量。
比如上面的inputs是长这样的。
{'input_ids': tensor([[ 0, 2264, 16, 5, 1948, 116, 2, 2, 1864, 35,
3394, 109, 47, 2813, 7, 3078, 5, 529, 6, 925,
10530, 13262, 6, 925, 83, 2543, 873, 3713, 5166, 50,
925, 11452, 415, 3303, 9056, 337, 116, 83, 35, 5,
200, 65, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]), 'token_type_ids': tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]), 'attention_mask': tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]), 'offset_mapping': tensor([[[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 4],
[ 5, 7],
[ 8, 11],
[ 12, 18],
[ 18, 19],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 1],
[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 6],
[ 7, 9],
[ 10, 13],
[ 14, 18],
[ 19, 21],
[ 22, 30],
[ 31, 34],
[ 35, 42],
[ 42, 43],
[ 44, 46],
[ 47, 56],
[ 57, 61],
[ 61, 62],
[ 63, 65],
[ 66, 67],
[ 67, 69],
[ 69, 71],
[ 72, 74],
[ 74, 77],
[ 78, 80],
[ 81, 83],
[ 84, 88],
[ 88, 90],
[ 91, 93],
[ 93, 96],
[ 96, 98],
[ 98, 99],
[100, 101],
[101, 102],
[103, 106],
[107, 113],
[114, 117],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, 0]]])}
offset_mapping是一个[batch_size, 128, 2]的变量。
而inputs.sequence_ids(0)则是一个[128]的数组,有点像token_type_ids。
[None,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
None,
None,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None]
将数据输入模型,可以得到两个输出sequence_output和pooled_output。
offset_mapping = inputs.pop("offset_mapping")
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = roberta(**inputs)
sequence_output = outputs[0]
pooled_output = outputs[1]
pooled_output结构是[1, 768],一般是用来做意图识别或者分类任务的,即针对[CLS]进行处理。
sequence_output的结构是[1, 128, 768],是针对每个token进行分类任务,比如之前的槽位识别。
针对这次的任务,我们也是要做类似于槽位识别的任务,判断答案的开始和结束。
将sequence_output传入线性层,输出就是[1, 128, 2]的数据。
logits = qa_outputs(sequence_output)
# [1, 128, 2]
logits
将logits拆分成start_logits和end_logits。
start_logits, end_logits = logits.split(1, dim=-1)
start_logits = start_logits.squeeze(-1).contiguous()
end_logits = end_logits.squeeze(-1).contiguous()
接下来就是计算交叉熵损失
loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=ignored_index)
start_loss = loss_fct(start_logits, start_positions)
end_loss = loss_fct(end_logits, end_positions)
total_loss = (start_loss + end_loss) / 2
如何计算start_positions呢?start_positions其实是每个样本的真实类别索引。
比如在上下文中,正确答案Dr Aftab Moosa的起始位置是63和77,由此计算出对应的token位置是从23到28。
start_index, end_index = 63, 77
sp = None
ep = None
for idx, (offset_start, offset_end) in enumerate(offset_mapping[0]):
# the QA_QUESTION will take 8 postions in offset_mapping
if idx < 8:
continue
if offset_start <= start_index < offset_end:
sp = idx
if offset_start < end_index <= offset_end:
ep = idx
我们也可以验证一下查到的token对不对。
predict_answer_tokens = inputs['input_ids'][0, sp : ep + 1]
tokenizer.decode(predict_answer_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True).strip()
# 'Dr Aftab Moosa'
计算交叉熵
start_positions = torch.tensor([sp], dtype=torch.long)
end_positions = torch.tensor([ep], dtype=torch.long)
loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=128)
start_loss = loss_fct(start_logits, start_positions)
start_loss # tensor(5.4668, grad_fn=<NllLossBackward0>)
end_loss = loss_fct(end_logits, end_positions)
end_loss # tensor(4.4615, grad_fn=<NllLossBackward0>)
交叉熵损失的计算步骤
首先针对每个token进行softmax概率计算
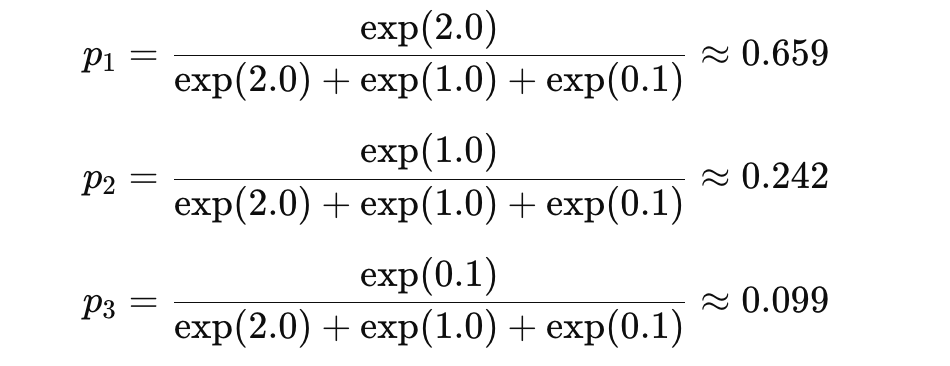
其次,针对target(假设这里是0),计算交叉熵损失。
−log(0.659)≈0.417