继续自己的刷题之旅 - Spaceship Titanic
题目
和泰坦尼克号类似,这次是飞船上的人被随机的传送走了,需要预测哪些被传送了。
查看数据
train_data = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
train_data.head()
| PassengerId | HomePlanet | CryoSleep | Cabin | Destination | Age | VIP | RoomService | FoodCourt | ShoppingMall | Spa | VRDeck | Name | Transported | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0001_01 | Europa | False | B/0/P | TRAPPIST-1e | 39.0 | False | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | Maham Ofracculy | False |
| 1 | 0002_01 | Earth | False | F/0/S | TRAPPIST-1e | 24.0 | False | 109.0 | 9.0 | 25.0 | 549.0 | 44.0 | Juanna Vines | True |
| 2 | 0003_01 | Europa | False | A/0/S | TRAPPIST-1e | 58.0 | True | 43.0 | 3576.0 | 0.0 | 6715.0 | 49.0 | Altark Susent | False |
| 3 | 0003_02 | Europa | False | A/0/S | TRAPPIST-1e | 33.0 | False | 0.0 | 1283.0 | 371.0 | 3329.0 | 193.0 | Solam Susent | False |
| 4 | 0004_01 | Earth | False | F/1/S | TRAPPIST-1e | 16.0 | False | 303.0 | 70.0 | 151.0 | 565.0 | 2.0 | Willy Santantines | True |
特征处理
拆分舱位
由于Cabin是按照特定的格式组合在一起的,先拆分成 3 个特征。
train_data[['deck', 'num', 'side']] = train_data['Cabin'].str.split('/', expand=True)
填充空值
对于奢侈消费,没有记录的,我们直接填 0
train_data[['VIP', 'CryoSleep', 'FoodCourt', 'ShoppingMall', 'Spa', 'VRDeck']] = train_data[['VIP', 'CryoSleep', 'FoodCourt', 'ShoppingMall', 'Spa', 'VRDeck']].fillna(value=0)
类型转换
由于树模型只能接受数值型数据,所以需要做转换,对于 Boolean 需要转换为 int,对于 string 要进行独热编码。
train_data['Transported'] = train_data['Transported'].astype(int)
train_data['VIP'] = train_data['VIP'].astype(int)
train_data['CryoSleep'] = train_data['CryoSleep'].astype(int)
train_data[['HomePlanet', 'Destination', 'deck', 'side']] = train_data[['HomePlanet', 'Destination', 'deck', 'side']].astype('category')
train_data['num'] = pd.to_numeric(train_data['num'], errors='coerce').astype('Int64')
category_data = pd.get_dummies(train_data[['HomePlanet', 'Destination', 'deck', 'side']])
删除不需要的特征
对于 PassengerId、Name 和 Cabin,我们都不需要了。
train_data = pd.concat([train_data.drop(['HomePlanet', 'Destination', 'deck', 'side'], axis=1), category_data], axis=1)
train_data = train_data.drop(['PassengerId', 'Name', 'Cabin'], axis=1)
train_data.head()
| CryoSleep | Age | VIP | RoomService | FoodCourt | ShoppingMall | Spa | VRDeck | Transported | num | ... | deck_A | deck_B | deck_C | deck_D | deck_E | deck_F | deck_G | deck_T | side_P | side_S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 39.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | ... | False | True | False | False | False | False | False | False | True | False |
| 1 | 0 | 24.0 | 0 | 109.0 | 9.0 | 25.0 | 549.0 | 44.0 | 1 | 0 | ... | False | False | False | False | False | True | False | False | False | True |
| 2 | 0 | 58.0 | 1 | 43.0 | 3576.0 | 0.0 | 6715.0 | 49.0 | 0 | 0 | ... | True | False | False | False | False | False | False | False | False | True |
| 3 | 0 | 33.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1283.0 | 371.0 | 3329.0 | 193.0 | 0 | 0 | ... | True | False | False | False | False | False | False | False | False | True |
| 4 | 0 | 16.0 | 0 | 303.0 | 70.0 | 151.0 | 565.0 | 2.0 | 1 | 1 | ... | False | False | False | False | False | True | False | False | False | True |
5 rows × 26 columns
训练
拆分训练集和测试集
y = train_data['Transported']
X = train_data.drop(['Transported'], axis=1)
X_train,X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, stratify = y, random_state=20)
网格搜索
xgb_model = XGBClassifier()
param_grid = {
"max_depth": [3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
"learning_rate": [0.1, 0.07, 0.05, 0.03, 0.01],
'n_estimators': [10, 50, 100, 200, 300]
}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(
estimator=xgb_model,
param_grid=param_grid,
cv=5,
n_jobs=-1,
scoring='accuracy'
)
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Best parameters: ", grid_search.best_params_)
print("Best score: ", grid_search.best_score_)
Best parameters: {'learning_rate': 0.1, 'max_depth': 4, 'n_estimators': 200}
Best score: 0.8064418228178061
测试
y_pred = grid_search.best_estimator_.predict(X_test)
y_pred
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)
Accuracy: 0.8257619321449109
验证超参
如果想要挑战一下超参,可以试一试,拿到的结果是一样的。
xgb_model = XGBClassifier(max_depth=4, learning_rate=0.1, n_estimators=200, eval_metric=['error'])
xgb_model.fit(X_train, y_train, eval_set=[(X_train, y_train)], verbose=True)
y_pred = xgb_model.predict(X_test)
y_pred
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)
# Accuracy: 0.8257619321449109
查看特征的重要性
feature_importance_map = zip(X_train.columns, grid_search.best_estimator_.feature_importances_)
sorted_feature_importance = sorted(feature_importance_map, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
# 打印排序后的特征和其重要性
for feature, importance in sorted_feature_importance:
print(f"Feature {feature}: Importance = {importance}")
Feature CryoSleep: Importance = 0.4743025302886963
Feature HomePlanet_Earth: Importance = 0.1131131500005722
Feature HomePlanet_Europa: Importance = 0.051258884370326996
Feature side_S: Importance = 0.03338198363780975
Feature VRDeck: Importance = 0.030072659254074097
Feature Spa: Importance = 0.028961313888430595
Feature deck_E: Importance = 0.028648849576711655
Feature RoomService: Importance = 0.025325145572423935
Feature side_P: Importance = 0.020662162452936172
Feature deck_B: Importance = 0.02019093744456768
Feature FoodCourt: Importance = 0.018049659207463264
Feature ShoppingMall: Importance = 0.016254669055342674
Feature HomePlanet_Mars: Importance = 0.01594861038029194
Feature deck_G: Importance = 0.015066892839968204
Feature deck_C: Importance = 0.014225861988961697
Feature deck_F: Importance = 0.013585352338850498
Feature Destination_TRAPPIST-1e: Importance = 0.01324284728616476
Feature Destination_55 Cancri e: Importance = 0.01319877989590168
Feature num: Importance = 0.012372505851089954
Feature Destination_PSO J318.5-22: Importance = 0.012308042496442795
Feature deck_A: Importance = 0.011042309924960136
Feature Age: Importance = 0.010368851944804192
Feature VIP: Importance = 0.004953885450959206
Feature deck_D: Importance = 0.0034641530364751816
Feature deck_T: Importance = 0.0
提交预测结果
test_data = pd.read_csv('test.csv')
passenger_ids = test_data.PassengerId
test_data[['deck', 'num', 'side']] = test_data['Cabin'].str.split('/', expand=True)
test_data[['VIP', 'CryoSleep', 'FoodCourt', 'ShoppingMall', 'Spa', 'VRDeck']] = test_data[['VIP', 'CryoSleep', 'FoodCourt', 'ShoppingMall', 'Spa', 'VRDeck']].fillna(value=0)
test_data['VIP'] = test_data['VIP'].astype(int)
test_data['CryoSleep'] = test_data['CryoSleep'].astype(int)
test_data[['HomePlanet', 'Destination', 'deck', 'side']] = test_data[['HomePlanet', 'Destination', 'deck', 'side']].astype('category')
test_data['num'] = pd.to_numeric(test_data['num'], errors='coerce').astype('Int64')
category_data = pd.get_dummies(test_data[['HomePlanet', 'Destination', 'deck', 'side']])
test_data = pd.concat([test_data.drop(['HomePlanet', 'Destination', 'deck', 'side'], axis=1), category_data], axis=1)
test_data = test_data.drop(['PassengerId', 'Name', 'Cabin'], axis=1)
test_data.head()
y_pred = grid_search.best_estimator_.predict(test_data).astype(bool)
y_pred
output_df = pd.DataFrame({'PassengerId': passenger_ids, 'Transported': y_pred})
output_df.head()
output_df.to_csv('submission.csv', index=False)
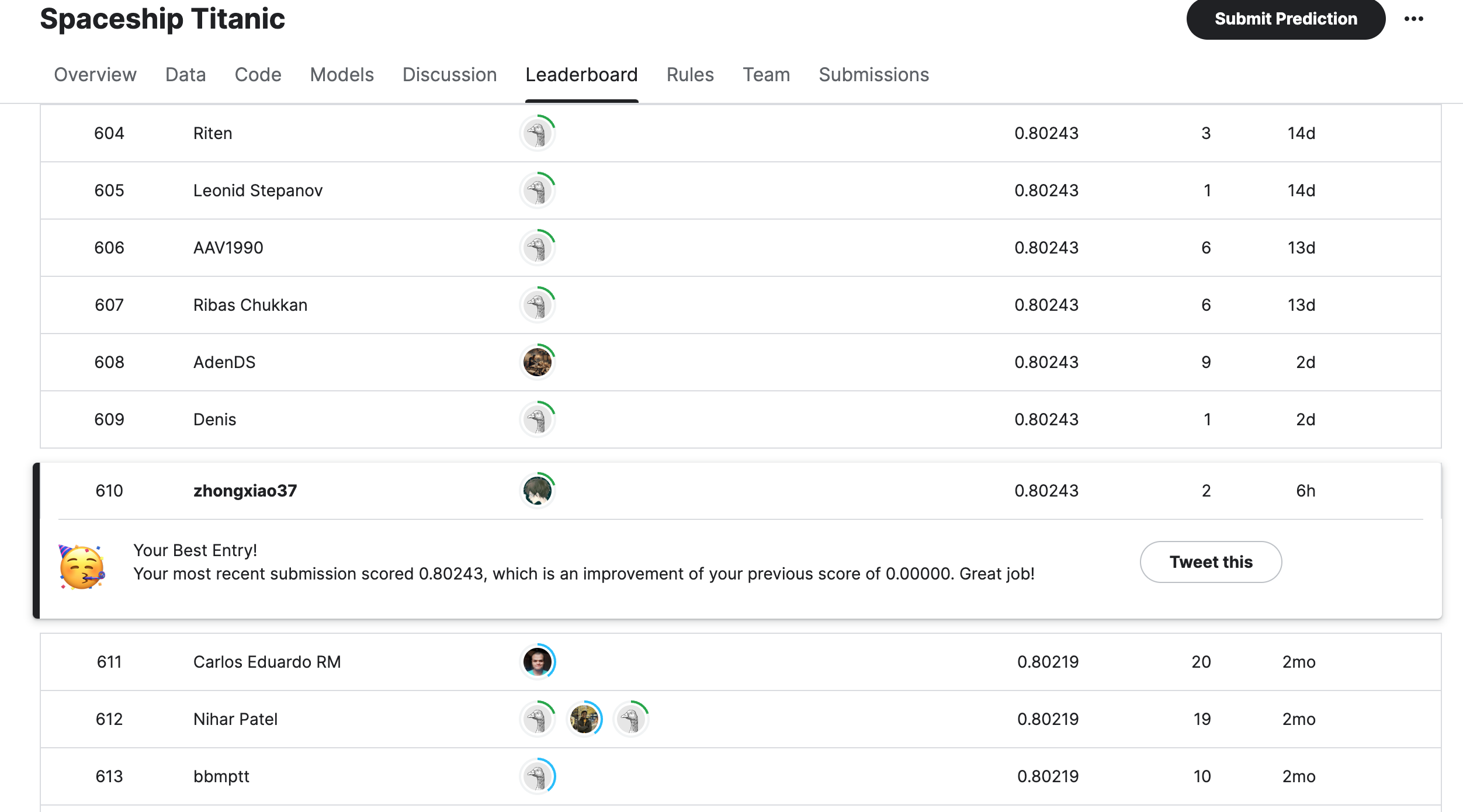
最后成功拿到 0.80243 的准确率,当期排名 610/2542。
自问自答
对于树模型,数值性特征是否需要分箱?
不,树模型能够自动处理数值型特征的非线性关系和阈值分割,因此不需要像线性模型那样对数值型特征进行分箱(也称为离散化或分段)来处理。树模型通过在每个节点选择最佳的分割点来构建树,因此它们能够有效地处理连续的数值特征。
对于 XGBClassifier,类别型数据如何处理
可以独热编码,也可以直接入模。
如果直接入模,需要指定enable_categorical=True且tree_method只能够是hist或者approx,这样做会丢失一些准确度。参见文档
xgb_model = XGBClassifier(tree_method='hist', max_depth=4, learning_rate=0.1, n_estimators=200, eval_metric=['error'], enable_categorical=True)
xgb_model.fit(X_train, y_train, eval_set=[(X_train, y_train)], verbose=True)
y_pred = xgb_model.predict(X_test)
y_pred
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)
# Accuracy: 0.8188614146060954
TensorFlow Decision Forests(TFDF)支持哪些数据类型?
TFDF 支持数值型,离散型(文字/类别),缺失值,但不支持布尔值,所以这些数据几乎不要特别的处理就可以直接喂给模型。
比如下面的代码,我们只需要对一些特征进行空值处理,将布尔值转换成数值型。
dataset_df = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
dataset_df = dataset_df.drop(['PassengerId', 'Name'], axis=1)
dataset_df[['VIP', 'CryoSleep', 'FoodCourt', 'ShoppingMall', 'Spa', 'VRDeck']] = dataset_df[['VIP', 'CryoSleep', 'FoodCourt', 'ShoppingMall', 'Spa', 'VRDeck']].fillna(value=0)
label = "Transported"
dataset_df[label] = dataset_df[label].astype(int)
dataset_df['VIP'] = dataset_df['VIP'].astype(int)
dataset_df['CryoSleep'] = dataset_df['CryoSleep'].astype(int)
dataset_df[["Deck", "Cabin_num", "Side"]] = dataset_df["Cabin"].str.split("/", expand=True)
dataset_df = dataset_df.drop('Cabin', axis=1)
dataset_df.head()
| HomePlanet | CryoSleep | Destination | Age | VIP | RoomService | FoodCourt | ShoppingMall | Spa | VRDeck | Transported | Deck | Cabin_num | Side | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Europa | 0 | TRAPPIST-1e | 58.0 | 1 | 43.0 | 3576.0 | 0.0 | 6715.0 | 49.0 | 0 | A | 0 | S |
| 4 | Earth | 0 | TRAPPIST-1e | 16.0 | 0 | 303.0 | 70.0 | 151.0 | 565.0 | 2.0 | 1 | F | 1 | S |
| 6 | Earth | 0 | TRAPPIST-1e | 26.0 | 0 | 42.0 | 1539.0 | 3.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1 | F | 2 | S |
| 7 | Earth | 1 | TRAPPIST-1e | 28.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1 | G | 0 | S |
| 8 | Earth | 0 | TRAPPIST-1e | 35.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 785.0 | 17.0 | 216.0 | 0.0 | 1 | F | 3 | S |
接下来转换一下就可以入模了。
def split_dataset(dataset, test_ratio=0.20):
test_indices = np.random.rand(len(dataset)) < test_ratio
return dataset[~test_indices], dataset[test_indices]
train_ds_pd, valid_ds_pd = split_dataset(dataset_df)
train_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(train_ds_pd, label=label)
valid_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(valid_ds_pd, label=label)
rf = tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel()
rf.compile(metrics=["accuracy"]) # Optional, you can use this to include a list of eval metrics
rf.fit(x=train_ds)
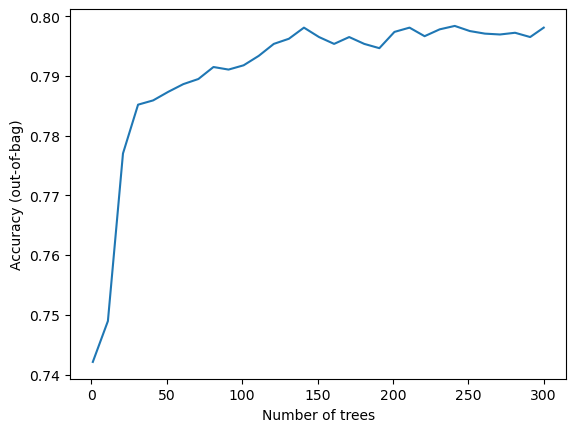
查看迭代过程
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
logs = rf.make_inspector().training_logs()
plt.plot([log.num_trees for log in logs], [log.evaluation.accuracy for log in logs])
plt.xlabel("Number of trees")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy (out-of-bag)")
plt.show()
查看一些常用指标
inspector = rf.make_inspector()
inspector.evaluation()
Evaluation(num_examples=6978, accuracy=0.798079678991115, loss=0.5250407830837662, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None, auuc=None, qini=None)
最后测试一下,得到的结果我们用 XGBClassifier 效果差不多。
evaluation = rf.evaluate(x=valid_ds,return_dict=True)
for name, value in evaluation.items():
print(f"{name}: {value:.4f}")
2/2 [==============================] - 6s 80ms/step - loss: 0.0000e+00 - accuracy: 0.8052
loss: 0.0000
accuracy: 0.8052